BlackRock, ARK Invest and WisdomTree submitted a revised Bitcoin spot ETF proposal yesterday, adopting the Cash Creation Method, which is the U.S. Securities Exchange Commission’s (SEC) preferred redemption method. The change marks an important shift for the industry and could herald the postponement of discussions on physical redemption options, a strategic move to streamline operations ahead of the Christmas holidays. Whether it is a physical redemption model or a cash redemption model, the Bitcoin spot ETF holds Bitcoin as its underlying asset, and the main difference lies in the redemption process. The SEC prefers the cash redemption model, because only the issuer will handle Bitcoin, avoiding the situation where unregistered broker subsidiaries handle Bitcoin.
But the cash redemption model in Bitcoin ETFs involves real cash flow, which may trigger tax liabilities such as capital gains tax, as it is considered Actual buying and selling activity. The physical redemption model directly exchanges Bitcoin for ETF shares, which does not involve the inflow and outflow of cash, so it is simpler in tax treatment and may avoid the tax burden caused by cash transactions. Let’s talk about these two redemption modes:
Physical redemption mode
Market maker (MM): a liquidity provider in the market. They are either registered U.S. securities broker/dealers subject to securities exchange regulation, or they are unregistered entities without a registered regulatory agency.
Authorized participant (AP): a financial institution authorized to create and redeem ETF shares, Usually done in large numbers of "creation units".
Listing exchange: The platform where ETF shares are traded.
ETF issuer: the company that manages the ETF.
Transfer Agent: A third party that handles the transfer of ETF shares.
Bitcoin custodian (e.g. Coinbase): The entity that holds custody of the ETF’s Bitcoin assets.
Spot cryptocurrency exchange: The place for instant delivery of Bitcoin trades.
The process of the trading day (T day):
Market makers request redemptions of ETF shares from authorized participants, particularly when the ETF's price deviates from its net asset value (NAV). Upon approval by the ETF issuer, the market maker acquires the shares for redemption.
On the next working day (T+1), they hand over these shares and the Bitcoin custodian releases the Bitcoins to them, which can be traded in the spot market For sale on. This pattern helps keep ETF prices consistent with Bitcoin’s market value.

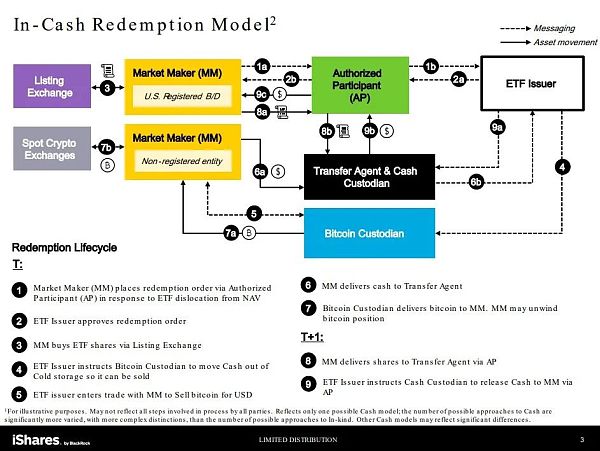
Cash redemption mode
Redemption order submission : Market makers, whether registered or not, submit orders to authorized participants to redeem ETF shares at a price below net asset value for the purpose of arbitrage.
Order approval: The ETF issuer approves the redemption request.
Buying ETF shares: Market makers purchase shares through the listed exchange.
Cash movement instructions: ETF issuers instruct Bitcoin custodians to prepare for use from cold reserves Sale for cash.
Transaction with ETF issuer: Issuer directly exchanges Bitcoin with market makers for US dollars .
Cash delivered to transfer agent: The market maker delivers cash to the transfer agent.
Bitcoin delivery: The custodian gives the Bitcoin to the market maker, who may sell it to obtain arbitrage profits.
Share delivery and cash release (next day): Market makers hand over shares for transfer The agent, the issuer, releases the cash to them, completing the entire process.
The reasons why the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) prefers the cash redemption model this time may also include the following points: First, the cash redemption model It is simpler in operation, makes the supervision process more direct and transparent, and facilitates effective monitoring and auditing by regulatory agencies. Secondly, this model can reduce the risk of large-scale redemption or purchase activities directly affecting the Bitcoin market price, thereby reducing the possibility of market manipulation. In addition, the cash redemption model helps better manage liquidity risks and provides greater flexibility and stability, especially when market volatility is high. Finally, considering the interests of protecting investors, the SEC believes that the cash redemption model can more effectively protect investors from the direct impact of price fluctuations of the underlying assets, especially in the highly volatile cryptocurrency market.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance







