Core Views
The Origin of "American Exceptionalism". "American Exceptionalism" represents a view that the US economy, politics and US dollar assets have unique advantages, which enable them to continue to outperform other markets in the global cycle. This view has been strengthened in 2023-2024. Behind the outstanding performance of US dollar assets, the advantages of the US economy, policies and technological development are indeed reflected. 1) Economy: The US economy maintains a high growth rate higher than the pre-epidemic level, and is "exceptional" immune to the scarring effect after the epidemic. 2) Policy: US fiscal stimulus "exceptional" breaks through traditional constraints and continues to be an important support for the economy. The Federal Reserve maintains a relatively high interest rate, but effectively avoids the economic and financial risks caused by high interest rates. 3) Technology:The leading position of the US in the field of science and technology has been highlighted in the new round of artificial intelligence (AI) development, and has catalyzed the strong performance of US stocks. 4) "Trump Trade":Trump's election once strengthened the "American Exceptionalism", making investors more confident in the US economy and US dollar assets.
The "American Exceptionalism" has reversed.In January and February this year, US stocks underperformed Hong Kong stocks and European stocks, and the US dollar index fell back. The capital market seems to have failed to trade the "Dollar Exceptionalism". 1) Economy: The most intuitive signal is that US economic data unexpectedly weakened and concerns about stagflation rose sharply.From the perspective of the Citi Economic Surprise Index, recent US economic data has been the most disappointing stage since Trump's election. As of February 28, the GDPNow model forecast value turned negative. 2) Trump's New Deal: Trump's tariff policy has amplified economic policy uncertainty and exacerbated concerns about stagflation. Trump's radical actions to streamline government agencies have hindered congressional budget negotiations and also implied economic downturn risks. The issue of cutting government spending and tariffs is closely linked to future tax cuts, reflecting the deep-seated contradictions in the US fiscal balance. The difficulty of implementing the US expansionary fiscal policy in the future may be higher than expected, which will then cast a shadow on the US economic outlook. 3) Technology: China's DeepSeek's breakthrough broke the expectation of US technology monopoly and catalyzed the adjustment of US stocks. In addition to China, Europe may also benefit from the reshaping of this technology competition landscape.
There is still room for global asset reallocation. The recent rapid reversal of "American exceptionalism" reflects the risk of excessive concentration of global funds in US dollar assets in the past two years or even longer.Since Trump took office, economic and political uncertainty in the United States has risen sharply. The U.S. economy may not be as strong as expected. The difficulty of fiscal balance in the United States and the negative effects that may be produced on the economy in the process of pursuing balance deserve further attention. The pattern of Sino-US and global economic, trade, technology and geopolitical games has also undergone important changes. Under these changes, investors may re-examine the long-term narrative of "American exceptionalism" that is difficult to disprove and adjust their regional allocation strategies. This process may not be "completed in one step" and may take a longer process. We believe that there is still a lot of room for global asset re-allocation. Since 2025, Chinese stocks (especially Hong Kong stocks) and European stocks have outperformed U.S. stocks, but they are far from making up for the huge gap in performance with U.S. stocks since 2020 (the impact of the new crown). The gap between China and the United States in AI and technology development is not significant. Considering the growth of the Chinese market, the valuation of high-quality companies in A-shares and Hong Kong stocks still has a lot of room to rise compared with U.S. stocks.
Risk warning:Trump's fiscal expansion exceeded expectations, the Fed's interest rate cut exceeded expectations, and the US's economic and trade restrictions on non-US regions exceeded expectations.
In 2023-2024, "American exceptionalism" became a major theme of global asset allocation, that is, US stocks continued to outperform non-US stocks and the US dollar remained strong. This reflects the advantages of the US economy, policies and technological development, and Trump's election once strengthened investment confidence in US dollar assets. However, since
2025, US stocks have underperformed non-US stock indices such as Hong Kong stocks and European stocks, and the US dollar index has also weakened. At present, since Trump took office, the economic and political uncertainty in the United States has risen sharply. The US economy may not be as strong as previously expected. The difficulty of fiscal balance in the United States and the negative effects that may be produced on the economy in the process of pursuing balance deserve further attention. The pattern of Sino-US and global economic, trade, technology, and geopolitical games has also undergone important changes. We believe that the investment theme of "the reversal of American exceptionalism" has not yet ended, and there is still a lot of room for global asset reconfiguration. 1.Origin of “American Exceptionalism”
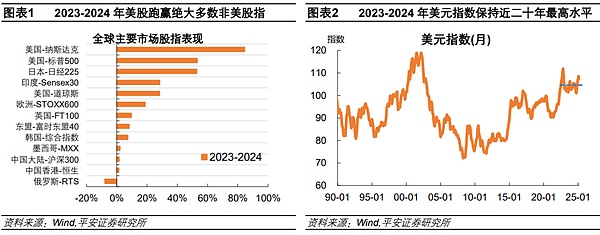
For investors, “American Exceptionalism” represents a view that the U.S. economy, politics, and U.S. dollar assets have unique advantages that enable them to continue to outperform other markets in global cycles. This view was strengthened in 2023-2024. In 2023-2024, the S&P 500 Index and the Nasdaq Composite Index rose by 53.2% and 84.5% respectively, performing better than the vast majority of non-US stock indices. At the same time, the US dollar index rose from 103 to 108, an increase of about 5%, and the volatility center remained at around 104 in the past two years, roughly at the highest level in nearly 20 years. Behind the outstanding performance of US dollar assets, the advantages of the US economy, policies and technological development are indeed reflected.
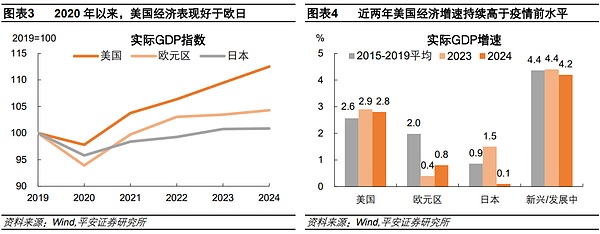
The U.S. economy maintained high growth above the pre-epidemic level and was "exceptional" immune to the scarring effect after the epidemic. Since 2023, the global economy has basically absorbed the impact of the COVID-19 epidemic and entered a "normalization" phase. However, the U.S. economy has shown remarkable resilience and unexpected growth during this period, showing the characteristics of "standing out from the crowd". In 2023-2024, the U.S. real GDP maintained a high growth rate of 2.8-2.9% for two consecutive years. During the same period, the real GDP of Europe and Japan grew by only around 1%. More importantly, the US economic growth rate in the past two years has not only recovered rapidly, but even exceeded the average level of 2015-2019 before the epidemic (2.6%). In contrast, the economic growth rates of Europe, Japan, and emerging market and developing economies are generally lower than the pre-epidemic level, showing varying degrees of "scarring effect".
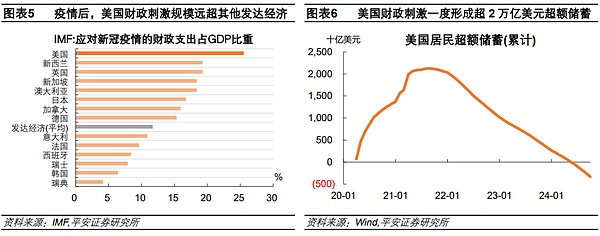
US fiscal stimulus "exceptional" broke through traditional constraints and continued to be an important support for the economy. After the outbreak, the United States' fiscal strength far exceeded that of other countries. This was influenced by the ideas of Modern Monetary Theory (MMT, and may have benefited from the flexibility and autonomy granted by the U.S. dollar's status as an international reserve currency. According to statistics from the IMF, the scale of fiscal support for the United States to cope with the impact of the new crown in 2020-2021 reached 25.5% of GDP, far exceeding the average level of developed economies of 11.7% and the average level of emerging markets of 5.7%. Among them, the fiscal "spending money" on residents has created more than 2trillion US dollars in excess savings, and continued to support residents' consumption from 2022-2024. After 2022, most countries in the world began to balance their fiscal deficits. However, according to the IMF, as of 2024, the U.S. deficit ratio will still have expanded by 3.7 percentage points from 2022 to 7.6%. leaf="">, while the eurozone deficit narrowed by 0.4 percentage points to 3.1% during the same period.
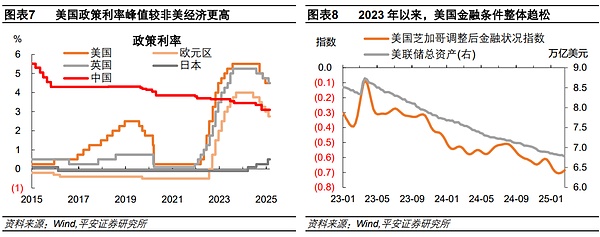
The Federal Reserve maintained a relatively high interest rate and effectively avoided the economic and financial risks caused by high interest rates. On the premise that the US economy maintains resilience, the US monetary policy maintains a higher interest rate level than other regions, and the higher return rate of US dollar assets attracts global capital inflows. Moreover, the market was once worried that high interest rates might trigger an economic recession, which was reflected in the alarm issued by the deep inversion of US bond interest rates. However, the damage of high interest rates to the US economy has not been apparent. One of the reasons is that the US government has effectively blocked the financial risks caused by high interest rates. Faced with the regional banking crisis in March 2023, the Federal Reserve and the Treasury Department immediately rescued the banks. The Federal Reserve briefly expanded its balance sheet by about 400 billion US dollars, which quickly restored stability to the financial market. Judging from the Chicago Fed Financial Conditions Index, the US financial system has actually tended to be loose since the regional banking crisis.
The United States' leading position in science and technology has been highlighted in the new round of development of artificial intelligence (AI, and has catalyzed the strong performance of U.S. stocks. Since the launch of ChatGPT in November 2022, the rapid breakthrough and widespread application of AI technology have undoubtedly been the key driver of the strength of US stocks. We discussed in detail the causes of the high concentration of US stocks in the report "Analysis of the Three Major Risks of US Stocks: Valuation, Concentration, and Macro". Benefiting from the AI theme and excellent profit realization ability, while the market value of the top US companies has increased, the share of these companies in the global stock market has also increased. According to Goldman Sachs statistics, the market value of the top ten US companies in 2024 will account for more than 20% of the world, reaching the highest level since the 1970s. This round of US stock technology wave is inseparable from the United States' continued investment in technology research and development, especially in the field of AI. According to OECD data, during the period 2021-2023, the United States' venture capital (VC) investment in the AI field was approximately US$200 billion, far exceeding other countries and regions. During the same period, China's investment was less than US$100 billion, and Europe's was less than US$100 billion. lang="EN-US">500US dollars.
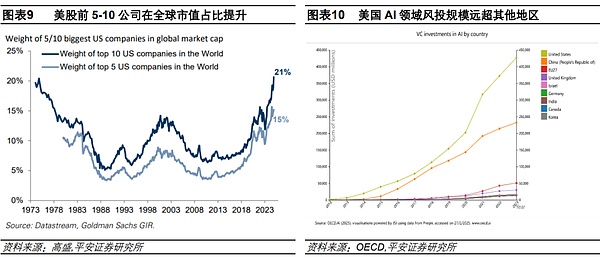
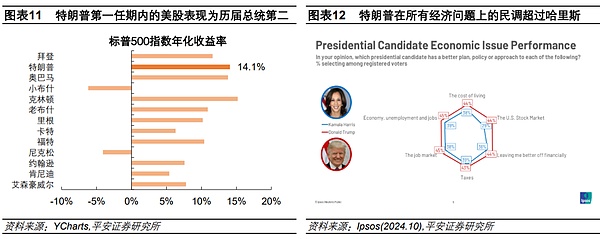
Trump's election once strengthened the "American exceptionalism", making investors more confident in the US economy and US dollar assets. Trump's "America First" policy logic is believed to be able to further support economic growth through tax cuts and deregulation, while tariffs and trade protection policies may further enhance the competitiveness of US companies, attract capital inflows, and form a "Trump cycle" similar to the "Reagan cycle" (reference report "From the "Reagan cycle" to the "Trump cycle": unchanged and changed"). During Trump's first term, the S&P 500 index had an annualized return of 14.1%, ranking second among all presidential terms since 1960, second only to Clinton. According to an Ipsos poll conducted one month before the election, the public believed that Trump would surpass the Biden-Harris administration on all economic issues, including employment, inflation, stock performance, etc.
2. “American Exceptionalism” Reversal
In January and February 2025, U.S. stocks underperformed Hong Kong and European stocks, the U.S. dollar index pulled back, and the capital market seemed to have failed to trade on the failure of “dollar exceptionalism”. So far this year (as of February 28), the S&P 500 index has only risen by 1.2%, and the Nasdaq index has turned to fall by 2.4%. At the same time, stock indices in China, Europe and other regions performed well, among which the Hang Seng Technology Index and the European STOXX600 Index rose by 24.6% and 10.4% respectively. The U.S. dollar exchange rate also showed some pressure. Since February (as of the 25th), the U.S. dollar index fell from above 108 to 106.3, the lowest point of the year, a drop of 2%. During the same period, the euro, yen and pound rose against the U.S. dollar by 1.6% respectively. First, the most intuitive signal is that the US economic data unexpectedly weakened and concerns about stagflation rose sharply. -0.2%), MarkitService industryPMI(49.7, expectedAt the same time, the latest inflation data were generally higher than expected, such as the US core CPI in January (up 0.4% month-on-month, expected 0.3%), core PPI (up 3.6% year-on-year, expected 3.6%). lang="EN-US">3.3%), etc. As of February 28, the GDPNow model predicts that in the first quarter of 2025, the U.S. GDP will turn negative at an annualized rate of -1.5% on a quarter-on-quarter basis. If the GDP growth rate in this quarter GDP has a negative growth month-on-month, which will be the first time since the first quarter of 2022 (when the Russian-Ukrainian conflict broke out). Secondly, Trump's tariff policy has amplified economic policy uncertainty and exacerbated concerns about stagflation. The recent US Economic Policy Uncertainty Index (EPU) has risen sharply to the highest level since the COVID-19 pandemic, and is significantly higher than Trump's first term from 2016 to 2019. On the one hand, the intensity and rhythm of tariff policies have been repeated. The tariff policy announced by Trump at the beginning of his term did not exceed expectations. For example, he only initially imposed a 10% tariff on China instead of the 50-60% promised during his campaign. In addition, there was room for negotiation and maneuver in the tariff policy, such as the postponement of the implementation of the first batch of tariffs on Canada and Mexico. However, in the near term, the negotiations between the United States and its trading partners seem to have made limited progress. Trump threatened to implement tariffs on Canada and Mexico as scheduled on March 4, and threatened to further impose 25% tariffs on the European Union, and increase tariffs on China from 10% to 20%. On the other hand, the tariff policy has strengthened the risk of stagflation. According to the latest estimates by PIIE, the Trump administration's 25%tariffs on Canada and Mexico and 10%tariffs on China (without considering countermeasures) may weaken U.S. GDP growth by about 0.3percentage point in the coming years and threaten U.S. GDPgrowth by 2025 leaf="">pushed up US inflation by 0.5 percentage points in 2017. The Michigan survey showed that US residents' inflation expectations rose significantly, while consumer confidence fell significantly, highlighting the impact of tariff policies on stagflation expectations.
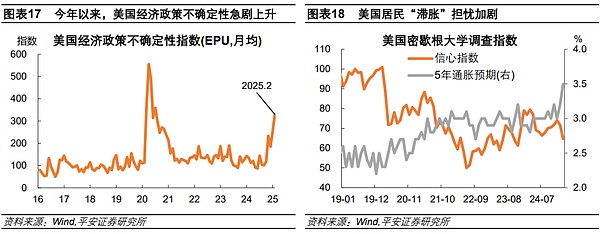
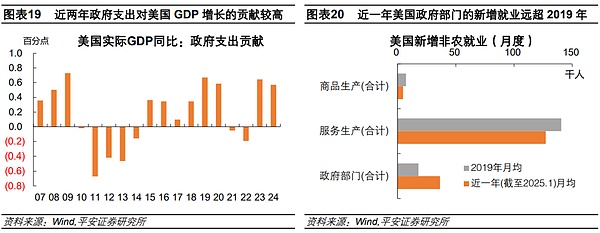
Again, Trump's radical actions to streamline government agencies have hindered congressional budget negotiations and also implied economic downside risks. The Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) led by Musk has taken vigorous actions in the past month, including large-scale layoffs, cutting "ineffective expenditures", and suspending foreign aid. As of February 21, DOGE's official website announced that since Trump took office, the department has helped save $55 billion in federal spending and more than 200,000 federal employees have been laid off. On the one hand, these actions have increased the difficulty of congressional budget negotiations and the risk of a government shutdown. The short-term spending bill passed in December 2024 will expire on March 14, 2025. If the U.S. Congress cannot pass a new appropriations bill or reach a budget agreement by then, the U.S. government will be shut down. Currently, the Democrats are opposed to Trump's radical cuts in government agencies and projects, making congressional negotiations more difficult. On the other hand, a sudden cut in government spending and employment could threaten the resilience of the U.S. economy and employment. In recent years, the direct pull of U.S. government spending on GDP growth has increased significantly, and the government's contribution to U.S. employment growth has increased significantly. In 2023-2024, U.S. government spending will contribute about 0.6 percentage points to GDP year-on-year, which is higher than the annual average of 0.4 percentage points from 2015 to 2019. In the past year (as of January 2025), the average monthly level of new non-farm employment in the U.S. government sector was 36,000 people, which is 2 times that of 2019.
Finally, the issues of cutting government spending and imposing additional tariffs are closely linked to future tax reduction policies, reflecting the deep-seated contradictions in the US fiscal balance. In 2018-2019, Trump's tariff policy did not cause a significant impact on the US economy and US stocks, mainly due to the implementation of the 2017tax reduction bill. But the situation is different this time. The pressure on the US fiscal balance has risen sharply. The Trump administration is trying to "increase revenue" through tariffs and "cut expenditure" by cutting government spending to create space for subsequent tax cuts. However, there is great uncertainty about the scale of tariff and government spending cuts, which makes the space for subsequent tax cuts less certain. Once the tax cuts are blocked, the "Trump cycle" may be discounted or ended ahead of schedule, and US stocks and the US dollar will also lose their original support.
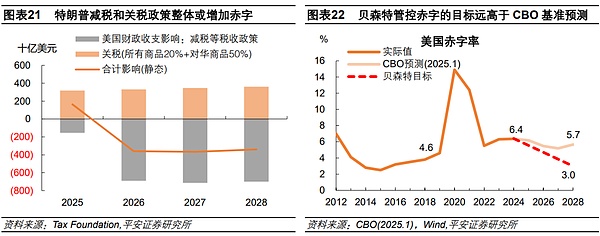
Looking deeper, the US fiscal situation may face a major shift during Trump's term. In fact, the US fiscal outlook is full of uncertainty. On the one hand, Trump's promotion of tax cuts will inevitably lead to reduced government revenue and pressure on deficit expansion. According to estimates by the Tax Foundation, Trump's tax cuts are expected to increase the deficit by around $700 billion each year from 2026 to 2029, and the radical tariff policy (20% global tariffs + 50% tariffs on China) will bring about $100 billion each year. Even if the budget revenue is 330-3800 billion US dollars, it will eventually lead to an annual deficit growth of more than 300 billion US dollars and an increase in the deficit ratio by about 1 percentage point. On the other hand, the new Treasury Secretary selected by Trump has proposed a goal of reducing the budget deficit ratio to 3% by 2028. The CBO's latest forecast in January 2025 showed that the U.S. deficit rate is expected to be 5.2-6.2% in 2025-2028, significantly higher than Bessant's target. Regardless of whether Bessant can successfully achieve the goal of reducing the deficit ratio, it can at least be considered that the road to fiscal balance in the United States is very difficult, and the difficulty of implementing the expansionary fiscal policy of the United States in the future may be higher than expected, which will then cast a shadow on the economic prospects of the United States.
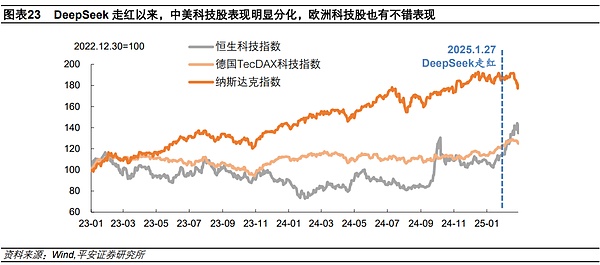
In addition, China's DeepSeekbreakthrough broke the expectation of US technology monopoly and catalyzed the adjustment of US stocks. Since DeepSeek became popular on January 27th (as of February 28th), the performance of Chinese and American technology stocks has diverged sharply, with the Hang Seng Technology Index rising by about 20% (the highest increase). The U.S. dollar index fell 28%, while the Nasdaq index fell about 6%. The rapid development of China's AI technology has shortened the technological gap between China and the world and the United States. Investors began to doubt that the United States' high investment in AI and its policy of containing competitors may not necessarily enable American companies to maintain their global leadership and monopoly. As the Rand Corporation of the United States commented, the DeepSeek-R1 (DS) model has quickly become one of the world's top large language models, fundamentally representing the failure of the US policy efforts to contain China's AI progress, especially by restricting chip sales. In addition, Europe may also benefit from the reshaping of this competitive landscape. 1month27days (as of2Month28), GermanyTecDAXTechnology stock index rose3% (the highest increase6%). An article from the Center for Strategic Studies (CSIS) in the United States pointed out that the success of DS may provide inspiration and guidance for European AI start-ups. European companies can learn from similar models, develop similar small-scale, low-cost models, and combine the advantages of European companies in privacy, security and regulatory compliance to develop more competitive AI products and services than American companies.
Third,There is still room for global asset reallocation
The recent rapid reversal of "American exceptionalism" reflects the risk of excessive concentration of global funds in US dollar assets in the past two years or even longer.Since Trump took office, economic and political uncertainties in the United States have risen sharply. The US economy may not be as strong as expected. The difficulty of fiscal balance in the United States and the negative effects that may be produced on the economy in the process of pursuing balance deserve further attention. The pattern of economic, trade, scientific and technological and geopolitical games between China, the United States and the world has also undergone important changes. Under these changes, investors may re-examine the long-term narrative of "American exceptionalism" which is currently difficult to disprove, and adjust their regional allocation strategies. This process may not be achieved in one step, and it may take a longer process.
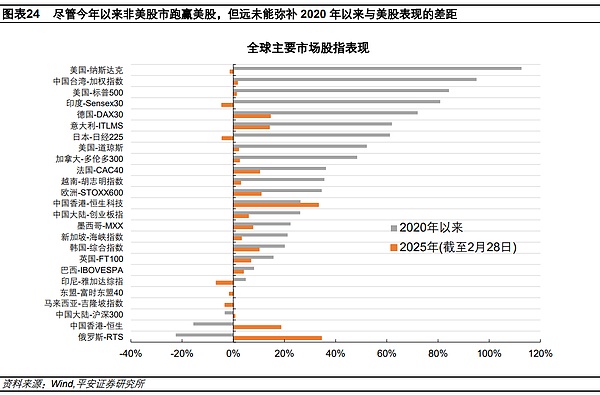
We believe that, at least from the performance of global stock markets, there is still a lot of room for global asset reallocation. Since 2025, Chinese stocks (especially Hong Kong stocks) and European stocks have outperformed US stocks, but they are far from making up for the huge gap in performance with US stocks since 2020(COVID-19 impact). Since 2020 (as of February 28, 2025), the Nasdaq Index and the S&P 500 Index have still risen by 113% and 5. leaf="">84%, the European STOXX600 index rose by 35%, the Hang Seng Technology Index rose by only 26%, the CSI 300 and Hang Seng Index still fell by 3% and 16%. leaf="">。
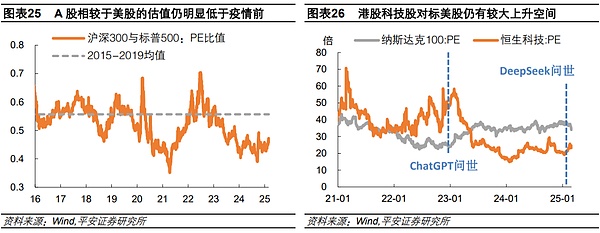
From the perspective of valuation, taking the Chinese and American stock markets as an example, as of February 28 this year, the Shanghai and Shenzhen 300 Index and the S&P 500 Index were both above 500. leaf="">PEThe ratio is only0.46, which is lower than2015-2019annual average level0.56. At the same time, the PE of the Hang Seng Technology Index is only about 23-25 times, which is significantly lower than the 34-37 times of the Nasdaq Index; it should be noted that for most of the time from 2021 to 2022, the valuation of the former was significantly higher than that of the latter, and at its highest it was twice that of the latter. Considering that the gap between China and the United States in AI and technology development is not significant, as well as the growth potential of the Chinese market, the valuation of high-quality companies in A-shares and Hong Kong stocks still has considerable room for growth compared with US stocks.
Risk warning: Trump's fiscal expansion exceeded expectations, the Fed's interest rate cut exceeded expectations, and the US's economic and trade restrictions on non-US regions exceeded expectations.
 Catherine
Catherine

















