The role of Blobs, Reorgs, and MEV-Boost
MEV Boost, Blob, The role of Blob, Reorgs and MEV-Boost Golden Finance, Analysis of the development and price stability of the Blob market
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
Author: Fu Shaoqing, SatoshiLab, All Things Island BTC Studio, Waterdrip
The rise of Bitcoin inscriptions has brought new vitality to the Bitcoin ecosystem, causing more people to start paying attention again Bitcoin, some say, has opened the Pandora’s box of the Bitcoin ecosystem. Among the many technical developments in the Bitcoin ecosystem, the construction of the second layer of Bitcoin is the top priority. In this direction, I drew on some well-known articles on the Internet, exchanges with many friends, and our team’s experience in the design and development of Web3 products, and summarized an article on the basic knowledge of the second layer of Bitcoin. This method is easy to summarize and learn, and because of the limitations of individual cognition, I hope it can attract more people to improve related ideas and allow this field to develop better.
The world of blockchain starts with Bitcoin and ends with Bitcoin ecology. (I personally agree with the summary of Mr. Dashan from Waterdrop Capital.) Ethereum is also a side-chain technology exploration of Bitcoin.
In this article, we will use "second-layer construction" or "second-layer network construction" mixedly. Usually, the term "second-layer network construction" is relatively narrow, and second-layer construction is a broader concept. However, in order to adapt to the common explanations such as layer 1 network and layer 2 network that are usually discussed in the industry, we will also use the concept of "layer 2 network construction". These two words are the same concept in this article.
In order to understand the basic problems that need to be solved in the construction of the second layer of Bitcoin. Let’s start by understanding the basic characteristics of the blockchain system.
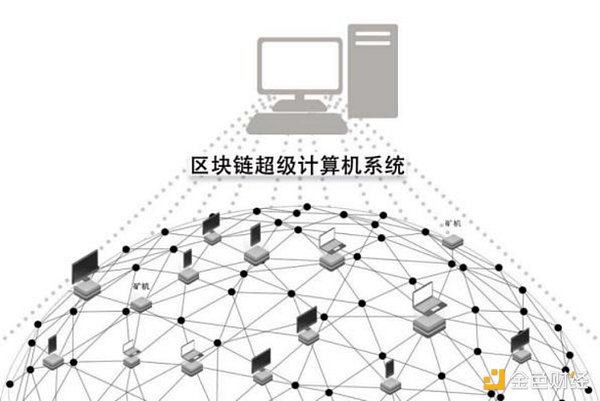
This article uses a concept proposed by Vitalik: Blockchain is a "world Computer”. It will be clearer for us to understand the various characteristics of blockchain from this perspective. In later chapters, we will also analyze the possibility of the development of this "world computer" based on the von Neumann structure in computers.
Let’s first summarize some basic features:
Notes:
In order to maintain the "world computer" of the blockchain "The demand generated by the normal operation of this "world computer" is called internal demand;
The demand to meet the needs of users who use this "world computer" is called external demand.
Open and transparent: This is the data storage and instruction execution characteristics of the "world computer" of the blockchain. It also requires the participation of many distributed nodes around the world. Computed internal demand characteristics. This feature just satisfies the user's right to know the data, and is the result of the internal collaboration requirements of the "world computer" itself and the external needs of the user. The privacy features mentioned later are to meet the external needs of users without destroying the collaboration requirements of the "world computer" itself.
Decentralization: This feature is the architectural feature of this "world computer". The degree of decentralization and fault tolerance are theoretically determined by the Byzantine Generals Theory ( Situations where there is a possibility of dishonesty among collaborators, i.e. situations where the agreement is not followed) are supported. Non-Byzantine general systems are not blockchain systems in theory. We will see two situations of non-blockchain systems in second-layer construction later. The degree of decentralization is an important indicator of blockchain security and is the basis for certain features.
Security:Security is composed of internal requirements generated by the architectural characteristics of this "world computer" and external requirements required by users. From the micro level, security is guaranteed by cryptography-related technologies, and from the macro level, it is ensured by the decentralization of the architecture, so that this "world computer" will not be affected by the forgery of micro data or the destruction of the macro architecture. security.
Computing power: One of the main functions of the world computer, blockchain, is computing power. To measure this indicator, we generally use it to examine whether it is Turing complete. In order to maintain their main characteristics, some chains are deliberately designed to be Turing incomplete. For example, in the Bitcoin network, Satoshi Nakamoto not only made its code instructions not Turing-complete, but also deliberately deleted some instruction sets during development to maintain its stability and security. All Turing complete technologies are designed to expand the computing power of the blockchain. From the perspective of layered design, simple systems are more suitable for the bottom layer.
Performance:With the same computing power, performance is another major capability when examining computers in the world of blockchain. It is generally measured by TPS, which is the number of transactions processed per second.
Storage: The blockchain is described as a "world computer", so it must have a storage function, which is the ability to record data. At present, it is basically stored in the block, and more professional on-chain storage outside the block is still under development.
Privacy:Privacy is a subdivided requirement in the "World Computer", which requires that the permissions of data producers and users be maintained during the calculation and storage process (we Put censorship resistance in the privacy section too). This is basically driven by the external needs of users.
There is also a comprehensive indicator, scalability, which generally refers to the scalability of the entire architecture. This feature affects most basic features. At the architectural level, the scalability of the system is a very important indicator. There will also be some other connection capabilities, or other capabilities for specific scenarios. I will not discuss them too much here. I will analyze them in detail when encountering these special scenarios.
Among the basic characteristics of these blockchains, most of them are restricted by the Impossible Triangle. For example, the DSS conjecture is decentralization (Decentralization, D), security (Security, S) and scalability (Scalability, S). As shown in the figure below:
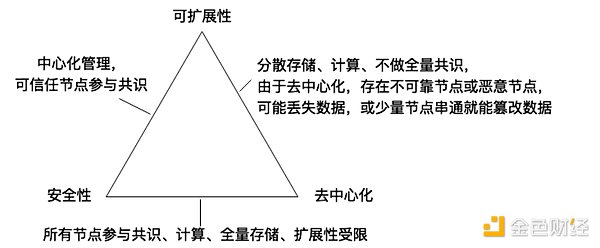
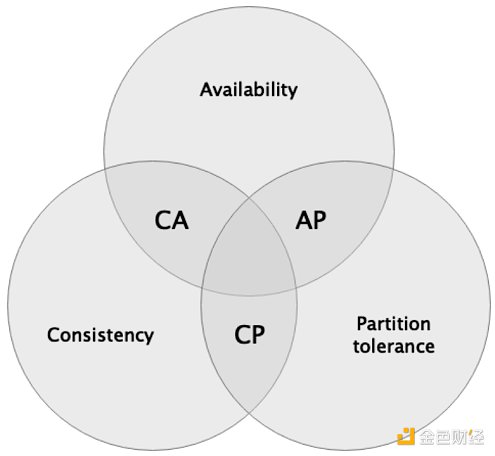
In distributed systems, a similar impossible triangle is the CAP principle. CAP refers to Consistency, Availability, Partition tolerance (partition fault tolerance) cannot be achieved at the same time. The blockchain system is a distributed system with Byzantine Generals Problem, so it also applies to the CAP principle.
The CAP principle is shown in the figure below:
What roles should the second-layer construction fulfill? What functions are provided? The second-floor construction must expand the deficiencies of the first-floor system. Things that are not suitable to be completed on the first-floor system can be completed on the second-floor construction.
We can draw a preliminary conclusion from the blockchain characteristics summarized above, which must be to expand these basic capabilities:Openness and transparency, decentralization, security, computing power, performance (throughput ), storage, privacy and more. In addition to these basic capabilities from a technical perspective, there is also a very important economic issue that needs to be solved, which is to reduce costs. Usually the overall cost of executing transactions on a one-tier network is relatively high, so a two-tier network is required. Reduce these costs.
To sum it up in one sentence: In order to increase capacity, reduce costs, and customize features, the three-dimensional solution is a two-story construction. As for the customization features, they are not obvious enough yet, or are often buried in the first two features and are somewhat confusing. We can understand that the characteristics of the first-layer network are required to different extents for many applications, and the implementation of various characteristics can be readjusted for certain applications on the second layer.
In the second-layer construction, the basic capabilities of the blockchain will have trade-offs, and some features will be reduced or even discarded in exchange for significant improvements in certain features. For example: in order to improve performance, some second layers will reduce the degree of decentralization and reduce security; in order to increase throughput, some second layers, such as the Lightning Network, will change the system structure and settlement method. Others will enhance certain features without reducing basic features, such as RGB processing, which obviously increases privacy and censorship resistance, but increases the difficulty of technical implementation. In later cases, we will see two-story construction that simultaneously reduces or alters several properties.
Reducing costs should be a basic requirement for all second-story construction. (Is there a second floor that does not reduce costs? I have not seen it yet.)
Hierarchical design is a means and methodology for humans to deal with complex systems. It divides the system into multiple hierarchical structures and defines the relationships and functions between each layer to achieve the system's Modularity, maintainability and scalability, thereby improving system design efficiency and reliability.
For an extensive and large protocol system, there are obvious benefits to using layering. This makes it easy for people to understand, easy to implement by division of labor, and easy to improve by modules. Such as the ISO/OSI seven-layer model design in computer networks, but in specific implementation, some layers can be combined. For example, the specific network protocol TCP/IP is a four-layer protocol. As shown in the figure below:
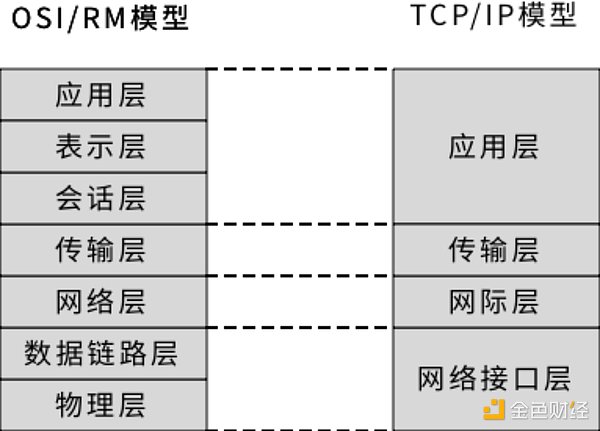
Figure 3-2 ISO seven-layer model and TCP/IP four-layer model
Specifically, the advantages of protocol layering:
1.Each layer is independent. A certain layer does not need to know how the layer below it is implemented, but only needs to know the services provided by this layer through the interface between layers. In this way, the complexity of the entire problem is reduced. In other words, how the work of the upper layer is performed does not affect the work of the next layer. In this way, as long as the interface remains unchanged when designing the work of each layer, we can adjust the working methods within the layer at will.
2.Good flexibility. When any layer changes, as long as the interface relationship between layers remains unchanged, the layers above or below this layer will not be affected. When there is a technological innovation in a certain layer or a problem occurs in the work of a certain layer, it will not affect the work of other layers. When troubleshooting, only the problems of this layer alone need to be considered.
3.Structurally separable. Each layer can be implemented using the most appropriate technology. The development of technology is often asymmetrical, and hierarchical division effectively avoids the barrel effect, and the overall work efficiency will not be affected by imperfect technology in one aspect.
4.Easy to implement and maintain. This structure makes it easier to implement and debug a large and complex system because the entire system has been decomposed into several relatively independent subsystems. When debugging and maintaining, each layer can be debugged independently to avoid the situation of not finding or solving the wrong problem.
5.Can promote standardization work. Because the functionality of each layer and the services it provides are precisely described. The advantage of standardization is that one of the layers can be replaced at will, which is very convenient for use and research.
The idea of hierarchical modular design is a common method in the technical field for dealing with a project that has a huge function and requires the cooperation of many people and continuous improvement of engineering projects. It is an effective method that has been tested in practice.
We take the second-layer construction of Bitcoin as a case to conduct relevant analysis. There are three obvious second-layer construction routes for the second layer of Bitcoin:
(1) One is a chain-based expansion route, which is very similar to the second layer of EVM and is a blockchain structure;
(2) One is based on a distributed route, represented by the Lightning Network, which is a distributed structure.
(3) There is also a route based on a centralized system, represented by a centralized index, which is a centralized structure.
The first two methods are very distinctive, and there are already some products in use and products under exploration. For the first method, due to the booming development of Ethereum and the exploration of other Bitcoin imitation chains, chain-based second-layer expansion is relatively easier, and there are more reference cases. The second distributed method is usually more difficult and develops slower, represented by the Lightning Network. The third method is very controversial because it does not look like a two-story building, but it seems to complete the function of a two-story building.
Which second-story construction plan is better? We use a market test result as a measurement indicator. Whichever second-tier network has a higher TVL (Total Value Locked), that plan is the optimal plan. With the development of time and technology, this optimal solution will be a process of change.
As for the definition of Bitcoin’s second-tier network, as long as it relies on the Bitcoin network, has a technical connection with the Bitcoin network, and has some features that are better than Bitcoin’s first-tier network, it is considered Bitcoin’s second-tier network. network construction. In other words, as long as BTC is consumed as gas, a system that uses BTC as the underlying asset and expands the performance of Bitcoin is considered a second-tier construction. Based on this judgment, we should recognize the third type of second-tier network construction, that is, the second-tier construction of a centralized structure.
The development of Bitcoin's own technology, such as modifying OP_RETURN, Taproot, Schnnor signature, MAST, and Tapscript, should be designed for the purpose of connecting the first and second layers, and excessive development functions of these technologies should not be used. , because no matter how much the first-tier network is expanded, there will be no qualitative breakthrough, and the second-tier network must be constructed. However, in the absence of better-used second-layer Bitcoin products, these technical capabilities that connect the first and second layers will be overused for a period of time.
Early Bitcoin imitation chains did a variety of explorations, such as "Colorcoin" (colored coins), " CovertCoins" and "MasterCoin"; various expanded Bitcoin imitation chains, such as BCH (Bitcoin Cash), BSV (Bitcoin SV), BTG (Bitcoin Gold); various side chain technologies are chain-based expansion construction cases that can It is said to be a second floor in a broad sense.
Including Ethereum, which is also an exploration of improvements based on Bitcoin. After convincing other project teams to no avail, Vitalik formed his own team to publish a white paper and develop a new generation of blockchain in view of the imperfections of Bitcoin: UTXO's accountless system, non-Turing completeness of the execution language, and poor scalability. Blockchain system. Although this kind of exploration of Ethereum is not a direct second-layer construction on Bitcoin, it is a kind of chain-based construction exploration in a broad sense.
Ethereum’s exploration of improvements to Bitcoin’s imperfections, as well as the development and verification of the second layer on Ethereum, provide a reference case for the development of chain-based second-layer networks on Bitcoin. Various Rollup solutions, cross-chain solutions, message channel technology, and Ethereum’s own sharding technology (From the perspective of the layered thinking of dealing with complex systems, perhaps this idea of solving multiple problems at one level is wrong), which makes the ecology of Ethereum technology flourish, and many people once believed that the development direction and future of the public chain have been determined, and the ecology represented by Ethereum has won. In fact, this is also based on the second layer of the chain. A manifestation of relatively mature construction. However, chain-based second-layer construction is only one method of second-layer construction. It has its own advantages and disadvantages, and other second-layer technologies are also needed to improve the entire second-layer ecology.
The chain-based second-layer construction in Bitcoin roughly includes two typical chain types, one is an EVM-compatible account model, and the other is a Bitcoin-like UTXO model. Existing cases (we use the generalized second-layer definition) include: Ethereum, Polygon, Bsc, Arbitrum, etc. are all EVM account models, and CKB (Nervos) and Chia are all UTXO models.
In the following chapters, some cases will be introduced in more detail when introducing the second-layer Bitcoin projects that have been implemented.
In addition, the second-layer projects that have been successful on Ethereum will also be added to the chain-based second-layer construction of Bitcoin. For these second-layer projects on Ethereum, the workload and challenges of transforming into the second layer on Bitcoin will be less. Based on the development and theoretical achievements of Ethereum's rollup maturity and modularity, this method of second-layer construction will become the mainstream of expansion discussions and is also the fastest-effective solution.
How successful will this transformation be? Developmental testing remains. We can make some preliminary judgments from the advantages and disadvantages of this chain-based second-layer construction.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of chain-based second-layer construction?
The disadvantage of this solution is that the second layer based on the chain is generally limited by the limitations of the blockchain, and the performance improvement is limited. Either the system becomes more centralized, or Lowering the block generation interval and increasing block capacity will generally reduce security. As a result, a two-story building above the second floor was born, which is the so-called Layer3 or Layer4.
The advantage is: this solution maintains most of the basic characteristics of the blockchain, and generally solves the problem of Turing completeness. The transaction costs are also significantly reduced, and it expands the first-layer network to a certain extent. Ability. Moreover, this solution has rich construction cases, and the technical implementation is relatively easy. There are already many exploration cases, and the migration of upper-layer applications is also very convenient. It is a faster implementation method. I believe this method will generate more second-level applications. layer network.
Roughly judged, due to the expansion limitations of this method, there should be many projects in the second layer based on the chain structure. There may be one or more second layers in each vertical field. Each project needs to Complete the second-story construction with your own characteristics to meet the needs of certain applications. Its value will also be determined by the number and total value of applications on it.
In the second-tier construction, there are also some constructions based on distributed systems. In this solution, the second-layer structure and framework are no longer blockchain structures, but a distributed system based on Channel. Lightning Network is a typical representative.
A distributed system consists of a limited set of processes and a limited set of channels. In order to deliver messages in a distributed system, the data, events, and channels that need to be controlled are already a relatively complex set of problems. The Channel we refer to here is the upper-level channel concept, such as the payment channel in the Lightning Network and the message channel in Nostr, rather than the underlying concept of the specific technology Channel in the distributed network.
The second-layer construction of distributed systems is divided into two categories:
(1) Only value transfer is completed, similar to the Lightning Network;
(2) It not only completes value transfer, but also completes Turing-complete technologies, such as RGB;
In the distributed two-layer construction solution, because it is value transfer, there are many difficulties beyond the original message transfer, such as The total value capacity within the channel, the rigor of the transaction, and the inability to consume it twice all exceed the difficulty of message delivery. Therefore, the development of distributed second-tier construction is not as fast as that of chain-based second-tier construction, and there are not many mature cases.
If you want to complete Turing-complete calculations on such a second layer, that is, build a Turing-complete virtual machine system on Channel, it will be even more difficult. Like the RGB protocol, it implements Turing-complete calculations on a distributed system through client verification and one-time sealing.
Existing cases of the second-layer construction of distributed distributed systems in Bitcoin include: Lightning Network, RGB, are there any more famous cases? If we look at it according to the standard of generalized two-layer construction, does Nostr also belong to the second-layer construction of distributed systems with Channel mechanism? When sorting out Ethereum information, I saw cases of using Channels in Ethereum documents: Connext, Raiden, and Perun, which can be used as exploration directions for in-depth researchers.
In the following chapters, the already running Bitcoin second-layer projects will be introduced, and the Lightning Network and RGB will be introduced in more detail.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of distributed systems based on distribution?
The advantages of this solution are generally that the system is more decentralized, the second-layer network can accommodate countless nodes, has better privacy and censorship resistance, and has unlimited scalability. Thus, theoretically the performance becomes extremely large.
The disadvantage of this solution is that the technical implementation is complex, and the routing algorithm, value splitting and encapsulation algorithms in a huge distributed system are relatively complex. Compared with information transfer, there is still a lack of engineering implementation experience and infrastructure in value transfer. This is also one of the reasons why the Lightning Network has been considered to be developing slowly.
In addition, it is a very big challenge to implement a Turing-complete system in this kind of system, that is, Channel+ computing. It can definitely be realized in theory, but in practice it is still in the early experimental stage. RGB is a typical representative of this situation.
Once a breakthrough is achieved in the second-layer construction based on distributed methods, it will greatly promote the development of upper-layer applications. The decentralization capabilities formed by its huge distributed nodes and the Turing-complete code execution capabilities will better support the next generation of Internet applications, which is the "Mass Adoption" scenario everyone is talking about.
Roughly speaking, there are generally only a few parallel projects on the second layer of a Channel-based distributed structure. There are two main reasons. One is the unlimited expansion capability of this system, and the other is The technical difficulty of implementation is high, so such a system needs to be more open in design and concept, and can accommodate more people and teams to participate. And based on this second-layer infrastructure application development team will also promote the development of this second-layer, for example, the RGB-based BiHelix project.
Do you need this classification? There should be controversy.
Centralized index structures like Ordinals or indexers of certain functional nodes are all centralized structures, and they are also a two-layer construction idea. However, this construction idea will be less recognized because the second layer is too centralized and the expansion of the first layer network is very limited. In the second-layer construction of this centralized structure, the basic characteristics of various blockchains depend on the first-layer network. The second layer only serves as some simple calculation and statistical functions. The second layer sometimes seems to be a dispensable The temporary existence can be replaced by another second floor at any time, and its importance does not seem to be that high. But from the perspective of On-Chain and Off-Chain, and from the perspective of improving the capabilities of the first-tier network, this centralized structure is also a second-tier extension.
In addition to Ordinals, examples of this kind of system should also include centralized exchanges. Projects in this situation will not be introduced in the following cases.
Advantages and disadvantages of the second-layer construction based on the centralized system:
The advantage is that the centralized system is very mature and has countless available cases and optimization solutions. Full Turing completeness and excellent performance.
The disadvantage is that the second layer is extremely centralized, and all the basic features of the blockchain depend on the first layer network.
Roughly speaking, there should be fewer projects on the second floor based on the centralized structure, or even phased ones. After the distributed structure based on chain structure and Channel matures and improves, most of the second-layer construction of centralized structures will disappear, or only centralized second-layers with fewer characteristic scenarios will remain. At the current stage, because the centralized system is very mature, it can well meet the scenarios of On-Chain data and Off-Chain calculations when it can write data on the basic chain. It is the easiest to implement for primary applications in the current Bitcoin ecosystem. pattern, is used extensively.
From the perspective of the above two-tier construction structure, there areblockchain System structure, Distributed system structure, Centralized system structure. This is our common classification of system structures: Centralized, Decentralized, Distributed. From this perspective, it is easier for us to understand the characteristics and applicable scenarios of each type. The three second-layer types all have their advantages and disadvantages. In the future complete Bitcoin ecosystem, all three types should be distributed according to different scenarios.
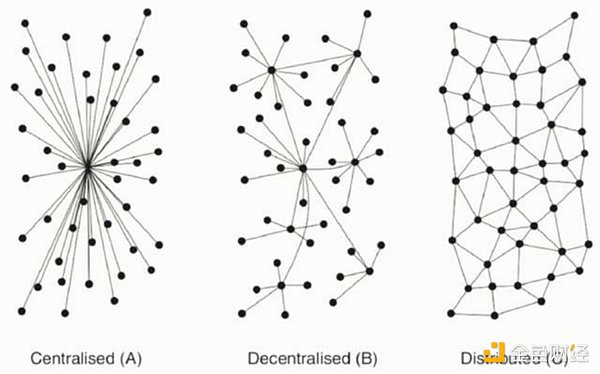
In addition The blockchain crowd often discusses Layer 3 or even Layer 4 above the second-layer construction, which is a generalized second-layer construction. Layer 3 and Layer 4 are completely different concepts from the 5-layer structure of the Web3 technology stack proposed by Gavin Wood. Layer3 and Layer4 in the Web3 technology stack are the classification methods of application protocols.
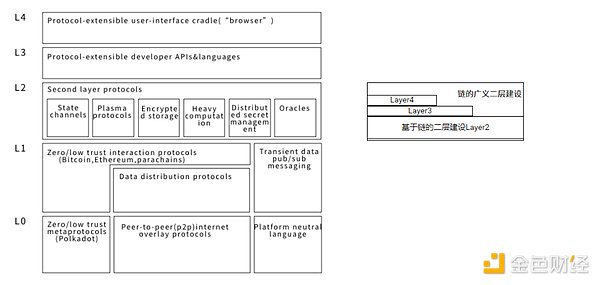
Gavin Wood's schematic diagram of the 5-layer Web3 technology stack and the generalized 2-layer construction of the chain
What impact will these second-layer constructions have on upper-layer applications? With the basic features provided by the blockchain system: Openness and transparency, decentralization, security, computing power, throughput, storage, privacy, etc., upper-layer applications will be built on these second-layer extensions on, and will intersperse interactions on these second layers. The second-layer expansion based on the blockchain structure, the second-layer expansion of the distributed structure, the second-layer expansion of the centralized structure, and some centralized applications will produce real, large-scale Web3.0 applications.
With the first-tier network and the second-tier construction, what is the connection between the two? Or are the two directly related? One is a direct technical connection, for example, a link through two-way locking or bridge technology. The other is correlation outside the system, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. Although there is no direct correlation, people transform BTC into WBTC to flow on Ethereum. There is not even any technical correlation, but individual adjustments based on price fluctuations. The positions of Bitcoin and Ethereum are a correlation outside the system.
Here we only discuss technical correlations. These correlation technologies are completely closely related to the structure and characteristics of the second layer. Later, we will refer to the von Neumann structure from a more macro perspective to judge the development of blockchain-related ecology.
We have already mentioned the development of Bitcoin itself, such as modifying OP_RETURN, Taproot, and Schnnor signatures , MAST, and Tapscript should all be designed for the purpose of connecting the first and second layers, and are the basic technical elements for connecting the first and second layers. These connection technologies are an important part of thinking about second-layer construction. BEVM’s first- and second-layer connections are representative to a certain extent, and most of them use the functions built with the above basic elements. The problem is similar in connecting to other Layer 2 systems.
These connection technologies will vary depending on the structure of the second-story building. Let me first introduce some link technologies in general. Common technologies for connecting the first-level network and the second-level network of blockchains include the following:
Cross-chain technology: Through cross-chain technology, different blockchains can Interoperate to realize the connection between the first-tier network and the second-tier network. Cross-chain technology can realize cross-chain transfer and interaction of assets, allowing data and value to flow between different blockchains.
Segregation Verification Technology: Segregation Verification technology can isolate transaction data in the first-tier network and then verify and process it through the second-tier network. This approach can reduce the burden on the first-tier network and improve overall throughput and efficiency.
Side chain technology: Side chain technology is a technology that connects the main chain and the side chain. The side chain can realize the connection between the first-layer network and the second-layer network. data transmission. Side chains can separate some specific functions and applications from the main chain to improve overall performance and scalability.
State ChannelTechnology: State Channel technology is a solution based on the second-layer network. By establishing a communication channel outside the chain, transactions can Do it off-chain and only submit to one layer of the network when needed. State Channel technology can increase transaction speed and throughput and reduce transaction fees.
PlasmaTechnology: Plasma technology is an expansion solution based on the second-layer network. It processes the transaction data of the first-layer network in slices and then Verification and processing are performed over a Layer 2 network, allowing for higher throughput and scalability.
Common two-layer structures include blockchain structure, distributed system structure, and centralized system structure. The common connection technologies above will vary depending on the structure of the second layer. Most can only be used in one structure and will not be discussed in depth here.
As second-story construction matures, there are more specific technologies or cases, and it may not even be a technical connection but only an economic connection.
What are the reference indicators for examining the quality of layer one and layer two link technology? The indicators you can roughly see are:
Can the first layer verify transactions on the second layer?
Can the assets on the first floor escape smoothly when the second floor collapses?
Will the connection technology degrade certain characteristics of the system?
…….
The content of the first- and second-layer link technology should be better summarized and improved when there are more cases of second-layer construction. These connection technologies are currently mostly completed by second-tier builders. It is difficult to say whether there will be independent products similar to cross-chain bridges in the future.
This section is more about raising questions and allowing us participants and builders to think more.
In the previous section, we have used the concept proposed by Vitalik:District Blockchain is a “world computer”. Since they can all be called computers, this "world computer" can be compared and analyzed with the von Neumann structure of traditional computers.

The Von Neumann structure of the blockchain, the "world computer" computer
The five major components of the Von Neumann structure computer:Operator , controllers, memories, input devices, and output devices. In the "world computer" system of blockchain, there are similar components, and we must also pay attention to the connection part among these five components, because in a distributed system, the connection part has a greater impact.
The development rules of "World Computer" are very similar to the development rules of traditional computers. Compared with the development of traditional computers, the blockchain system is still at a stage similar to that before 286. It is still expanding processing capabilities and storage capabilities. It has simple peripherals and is still very limited in what it can do.
Several comparisons between the development of traditional computers and the development of "world computers":
(1) The expansion of CPU (calculator and controller), just like the current one-level and two-level computers The expansion of layer computing energy and throughput;
(2) The expansion of memory will gradually shift from competing for space on the chain to using real blockchain storage. The current one- and two-layer on-chain storage spaces are like registers, first-level cache, and second-level cache in traditional computers. In the future, there will be professional blockchain storage methods such as memory, hard disk, and external storage. The current way of writing data will also change a lot in the future.
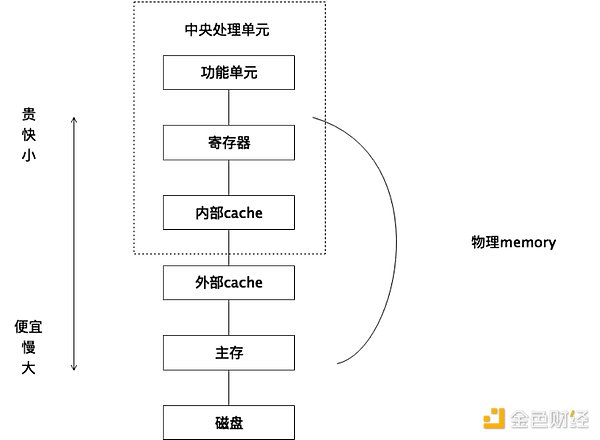
( 3) Input devices and output devices, in the blockchain system, are oracles. These input and output devices have not been reflected much in the second-floor construction, and there will be more demands in upper-layer applications.
(4) Some special chains and functions in the blockchain are very similar to the GPU, special equipment cards, special peripherals and other components in traditional computers.
(5) On-chain applications and higher-level applications, just like traditional computers that have not yet distinguished operating systems and application software, are also evolving and functionally separated step by step.
(6) Many of the current blockchain applications are financial applications, much like early traditional computers, which are mostly used for scientific research and military applications. With development, they are slowly moving towards enterprises and families. , towards the individual. Blockchain applications will have a similar development trend, developing from early financial applications to broader applications.
From the construction of the second layer, there is still a lot to discuss about comparing traditional computers and the "world computer" of the blockchain, which will not be described in this article.
In this article, we mainly introduce those second-layer Bitcoin projects that have been successfully operated, referring to some research reports and industry reports. These second-layer constructions have been running for a certain period of time, most of them from 2015-2019. To start brewing or launching. Some newer projects will also be introduced if they have special features. We will see that these cases are basically based on the second-layer construction of the chain, and the only distributed system construction based on the Channel is the Lightning Network. If you include the second-layer construction of Ethereum, Raiden Network is also a design case based on Channel, but its current development does not seem to be successful and will not be introduced in this article. Ethereum's Plasma technology is a design solution for a sub-chain based on Channel. It seems to be a combination of chain and Channel. I personally think that its main feature is a two-layer design based on chain, so I won't discuss it too much here.
1.Lightning NetworkLightning Network (based on distributed second-layer construction)
Lightning Network (Lightning Network) is a second-layer solution built on the Bitcoin blockchain and is designed to solve Bitcoin's scalability and low transaction speed problems. The Lightning Network was first proposed in 2015 and fully implemented in 2018.
The main features of the Lightning Network are fast, low-cost and scalable. It establishes a series of payment channels so that Bitcoin transactions can be conducted within the channels without being directly recorded on the blockchain. This can greatly reduce transaction confirmation time and transaction fees, and support a large number of parallel transactions. The Lightning Network relies on the RMSC protocol to ensure the safety and reliability of transactions, while HTLC solves the problem of routable scalability. The scalability of its architecture gives it very high performance.
Since its launch, the Lightning Network has received widespread attention and adoption. More and more Bitcoin users, exchanges and merchants are using the Lightning Network for fast cross-chain transactions and real-time payments. In addition, developers are constantly improving the performance and user experience of the Lightning Network, providing it with more features and scalability.
While the Lightning Network offers significant improvements in scalability and transaction speed, it still faces several technical and adoption challenges. For example, network stability, routing algorithms and user interfaces need to be continuously improved. However, as time passes and technology improves, the Lightning Network is expected to become an important payment solution for Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, providing users with a faster, lower-cost transaction experience.
2. Liquid(Chain-based second-layer construction)
Liquid is a side-chain launched by Blockstream in 2015. chain solution. As the first sidechain of Bitcoin, Liquid aims to provide faster, secure and private transaction solutions to meet the needs of professional users such as financial institutions and exchanges.
One of the main features of Liquid is its fast transaction confirmation time. Compared to Bitcoin’s confirmation time of about 10 minutes, Liquid’s transaction confirmation time is only 2 minutes. This enables users to conduct transactions faster and transfer funds quickly when needed. Another important feature is Liquid’s transaction privacy. Liquid uses Confidential Transactions (confidential transactions) technology to hide the transaction amount, and only the participants in the transaction can view the specific amount. This helps protect the privacy of transaction participants.
Liquid also has higher transaction throughput. By using Federated Peg (federal anchoring) technology, Liquid can support a large number of parallel transactions and anchor on the Bitcoin network to achieve interoperability with Bitcoin. This allows Liquid to handle more transaction volume and improve overall system throughput.
Since its launch, Liquid has gradually grown in the cryptocurrency industry. More and more exchanges, financial institutions and enterprises are beginning to adopt Liquid as their trading and fund settlement solution. At the same time, Blockstream continues to roll out new features and improvements to further improve Liquid’s performance and security.
In summary, Liquid is a Bitcoin sidechain solution launched by Blockstream that aims to provide fast, private and high-throughput transactions. It meets the needs of professional users by reducing transaction confirmation time, providing transaction privacy, and increasing transaction throughput. Over time, Liquid has become widely used and developed in the cryptocurrency industry.
3. Rootstock(RSK) (chain-based second-layer construction)< /p>
Rootstock (RSK) is a smart contract platform built on the Bitcoin blockchain and aims to provide Ethereum-like functionality to the Bitcoin ecosystem. Rootstock was first proposed in 2015 and officially launched in 2018.
The main feature of Rootstock is its two-way anchoring with Bitcoin and its smart contract function. With two-way anchoring to Bitcoin, Rootstock is able to use Bitcoin as its primary asset, achieving security and stability. At the same time, Rootstock supports smart contract functions, allowing developers to build and execute smart contracts with automation functions on its platform.
Since its launch, Rootstock has gradually gained recognition and adoption within the Bitcoin ecosystem. It provides more functions and flexibility to Bitcoin users and developers, allowing Bitcoin to support a wider range of application scenarios, such as decentralized finance (DeFi), digital asset issuance and supply chain management.
However, compared with other smart contract platforms, Rootstock’s development has been relatively slow. Its expansion in terms of user and developer communities requires more efforts. Nonetheless, Rootstock’s development prospects are still considered positive, and it has the potential to become one of the important smart contract platforms in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
4. RGB(based on distributed+Turing complete second-layer construction)
The story of RGB dates back to 2016, when Giacomo Zucco wanted to use Peter Todd’s concept of client-side verification and disposable seals to develop a better colored coin and Bringing these tokens into the Lightning Network (hence the name “RGB”). It is an open protocol built on the Bitcoin blockchain and aims to provide richer functions for the creation, trading and management of digital assets. RGB is a scalable and confidential smart contract system for Bitcoin and Lightning Network developed by the LNP/BP Standards Association. It adopts the concepts of private and common ownership and is a Turing-complete, trustless form of distributed computing that does not require the introduction of tokens and is a non-block decentralized protocol.
RGB is designed to run scalable, robust, and private smart contracts on UTXO blockchains (like Bitcoin) to make all possibilities possible. Through RGB, developers can execute token issuance, NFT minting, DeFi, DAO, and more complex multi-category smart contracts.
The RGB protocol is based on the concepts of client-side validation and single-use-seals, on the second and third layers of the Bitcoin ecosystem (chain client state verification and smart contract system running outside).
5. Stacks(Chain-based two-layer construction)
Stacks (formerly Blockstack) is a blockchain-based A decentralized computing platform based on the currency blockchain. Stacks was first proposed in 2013 and had an initial coin offering (ICO) in 2017. Its main feature is to provide decentralized authentication, storage and smart contract functions.
The core feature of Stacks is to support the development and execution of decentralized applications through the security and stability of Bitcoin. It uses a consensus mechanism called "Stacking" to achieve consensus by letting users holding STX tokens lock a certain number of tokens and participate in network verification. This mechanism provides incentives for users and increases the security of the network.
In terms of development, Stacks has become one of the important platforms in the field of decentralized applications. It has attracted a group of developers and projects to join, built numerous decentralized applications, and provided a wealth of tools and development documentation. Stacks also cooperates with other blockchain projects to expand its ecosystem and application scenarios.
6. Other Bitcoin second-layer projects
With the popularity of Bitcoin, many new projects have been produced. Among them, there are many projects initiated by Chinese, and these new projects such as B² Network, BEVM, Dovi, Map Protocol, Merlin, Bison, etc. also have certain characteristics.
B²Network was established in 2022. It is a second-layer Bitcoin network developed based on ZK-Rollup. It is compatible with EVM and enables EVM ecological developers to seamlessly deploy DApps. It is a typical case of transferring the second-layer technology of Ethereum technology to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
BEVM’s original team was established in 2017 and has explored a variety of extended applications of Bitcoin. The BEVM concept proposed in 2023 is a decentralized Bitcoin L2 compatible with EVM. BEVM is based on technologies such as the Schnorr signature algorithm brought by the Taproot upgrade, allowing BTC to cross-chain from the Bitcoin main network to Layer 2 in a decentralized manner. Since BEVM is compatible with EVM, all DApps running in the Ethereum ecosystem can run on BTC Layer 2 and use BTC as Gas. On November 29, 2023, BEVM released a white paper.
Dovi was founded in 2023 and is a Bitcoin Layer 2 compatible with EVM smart contracts. In November 2023, Dovi officially released a white paper. According to the white paper, Dovi integrates Schnorr signatures and MAST structures to improve transaction privacy, optimize data size and verification processes; issue a flexible framework for various asset types other than Bitcoin, and realize cross-chain asset transfers.
Map Protocol’s team was established relatively early. It originally focused on cross-chain protocols, which is the first- and second-layer connection technologies we introduced earlier. After the Bitcoin ecosystem became popular, it will soon be able to build a second-layer construction based on the chain. The ability to cross-chain current inscription assets and reduce transaction fees will attract some project parties and applications.
From the official website of Merlin Chain, it is easy to see the attributes of its Bridge. It transfers assets on BTC to the second-layer network and reduces transaction costs. It is a typical representative of solving pain points first. According to the official website introduction and some research reports, Merlin is a Bitcoin Layer 2 solution that integrates the ZK-Rollup network, decentralized oracles and on-chain BTC fraud prevention modules. The project was launched by Bitmap Tech, a unique team. The Bitmap.game and BRC-420 "Blue Box" Ordinals assets they launched have good reputations.
Founded in 2023, Bison is a Bitcoin-native zk-rollup that increases transaction speed while implementing advanced features on native Bitcoin. Developers can use zk-rollup to build innovative DeFi solutions such as trading platforms, lending services, and automated market makers. From its official website, Bridge is also an important function point. Cross-chaining Bitcoin assets and completing upper-layer asset applications is the entry point for many projects.
Judging from the above relatively new projects B² Network, BEVM, Dovi, Map Protocol, Merlin, and Bison, they have quickly completed the reduction of transaction fees and met the transaction needs of Bitcoin's first-level assets. They all involve cross-chain assets. Those teams that have cross-chain protocols can do it faster. Teams that have experience in second-layer construction have more advantages in upper-layer applications. These newer projects are all based on the second-layer construction of the chain, taking advantage of the original technology accumulation and short-term explosive power. These projects are somewhat homogeneous. What will be their future development? What will be the outcome of competition with distributed second-tier construction service providers? It also requires a lot of observation. Judging from the experience of second-tier projects on Ethereum, many projects will fall flat after the tokens are issued through hot-spot marketing. Will this be the case for Bitcoin's second-tier projects?
From the projects currently running on the second layer of Bitcoin, we can roughly see that the well-known second-layer Bitcoin projects were established relatively early and have been exploring related technologies for a long time. However, because of the The basic technology has not been formed, and most of the projects are not exciting enough, or they are overshadowed by the light of Ethereum and the Ethereum ecosystem. With the maturity of Bitcoin's basic protocols, especially the formation of underlying technologies such as Segregated Witness, Taproot, Schnorr signatures, MAST Merkle abstract syntax tree, and Tapscript, the connection technology between the first layer and the second layer has developed better. As a result, the things that the Bitcoin ecosystem can do are becoming richer. From the second-layer projects of Bitcoin that are already running, we can see that some are builders of the original Bitcoin ecosystem, another part are builders of the second layer of Ethereum, and some are builders from connection technology. No matter which direction the project comes from, it needs to use these newly generated Bitcoin basic connection technologies. The more fully and diversified the methods of use are, the better the support for the second layer will be.
Wherever the funds are, the popularity will be there, and it will attract more funds to gather. Bitcoin currently has a market value of approximately US$800 billion. Its ecological development is weak, but it has the potential to explode. Therefore, many projects claim to carry out the second-layer construction of Bitcoin. We will not mention the specific names of these projects here, but we will make some classifications of the entrants of these projects to see their characteristics and their respective advantages and disadvantages.
1. Original Bitcoin second-layer construction project
The original Bitcoin second-layer project, especially the one that has been developed for many years, has Can certain accumulated advantages be rejuvenated by the popularity of Bitcoin? Will it thrive? There is great uncertainty.
There are two measurement criteria: First, as mentioned earlier, whichever second-layer network has a higher total locked-up value TVL will win out. The other is the two-layer structure type. The chain-based two-layer construction will accommodate more parallel players because of its expansion characteristics. The distributed two-layer construction can only accommodate relatively few competitors.
The original second-tier projects still need to give full play to their accumulated advantages and establish new advantages with the help of new technologies to attract more applications to the platform. Only then can they have the opportunity to rejuvenate and strive for more market share. If it fails to attract more applications, such old projects are likely to eventually sink or transform. In fact, such projects can also cooperate or merge with projects that have no technical accumulation at all and have established a community through some consensus through some consensus in exchange for greater development.
In addition, if those old projects can have advantages in the accumulation of distributed-based second-tier construction technology, they can fully intervene in the distributed-based second-tier construction, and it will be more effective by providing guidance for upper-layer applications.
2. Newly entered Bitcoin second-tier construction projects
Newly entered Bitcoin second-tier construction projects generally do not have many accumulated advantages, but This gives such a team the advantage of being a latecomer. They can research the latest technologies, solve the lightweight and most attractive needs first, and attract a certain number of applications. It is best to have a team with second-layer construction experience in the Ethereum ecosystem or other ecosystems, which is more suitable for quickly entering the second-layer construction of Bitcoin. For such a project, you can consider chain-based second-layer construction, which will be faster and more advantageous.
Teams with no experience or advantages at all can refer to the third situation to see if they can screen out users and accumulate funds through community consensus.
3. Bitcoin second-layer projects that have no experience but want to enter
I originally promoted that I wanted to enter Web3 without any technology accumulation or community accumulation. .0 projects, I don’t have much understanding, and I will most likely regard these projects as CX projects. But through the phenomenon of inscriptions, those communities that have generated a large community consensus through a certain inscription, such as sats, ordi, and rats, not only have many members, but also accumulated a certain amount of funds. Such a project can completely start a new second-layer construction from scratch. Through the power of the community, upper-layer applications can be integrated into the community. At the same time, it is possible to build a second-layer. Such a second-layer will most likely be chosen to be chain-based. The second-layer construction is simple and fast, and through the power of the community, DID (decentralized identity), DAO tools, DeFi applications, and other upper-layer applications are built on the second layer of the community, and there is no need to build it yourself, only need to introduce it Mature product parties and share revenue sharing with them. This may form a small ecology. Such projects place higher demands on community construction, foundation management, and decision-making mechanisms.
4. Development of upper-layer applications
With the rapid development of the second layer of Bitcoin, the huge amount of funds sleeping on BTC began to be reawakened, and Because of the eyeball effect, more new users will be attracted to enter the Web3.0 field. Coupled with the rapid development of Bitcoin's second-layer technology, it will lay a solid foundation for Mass Adoption. The upper-layer applications will start from the current financial applications and gradually introduce applications that require high performance, large traffic, and frequent interaction, such as Gamefi, SocialFi and other applications. There will be no downtime of chain-based applications and poor service experience. Good situation. The development of Bitcoin's second layer will bring many opportunities and solid infrastructure to upper-layer applications. When mature, it will bring more opportunities to more less-Native Web3 teams.
In any case, the Web3.0 era has just begun. It is still in its infancy and early stages and requires a lot of exploration and construction. Many countries and regions are not yet fully open to many new things in Web3.0. . Web3.0 requires a lot of construction and will give each project team more opportunities. A team that constantly senses new developments and new technologies, constantly adjusts, and constantly participates in the construction of Web 3.0 will definitely gain something at a certain stage and in a certain field.
Writing this article is the result of my reading a large number of industry articles and participating in many activities such as TwitterSpace and offline communication. Inspired by the speeches of many people, some prominent influencing people and factors are as follows:
(1) Mr. Dashan from Waterdrop Capital, he has written many articles and also gave us a He gave many lectures and participated in many Space activities that he participated in.
(2) Some in-depth technical content is obtained by listening to Teacher Hong Shuning’s lectures, watching his videos, and communicating with Teacher Hong Shuning offline, such as routing issues in distributed systems, RGB Turing completeness question.
(3) Numerous articles on www.btcstudy.org. There is a wealth of knowledge compiled on this website.
(4) Interview program with Jan Xie, chief architect of Nervos (CKB).
(5) Read more about BIP protocol, Segwit, Taproot, ordinals, brc20, Atomical, etc.
(6) Other blockchain knowledge, including hierarchical design ideas and comparison of von Neumann structures, are derived from the accumulation of knowledge I wrote in several books in the past few years, of which 5 were published. "Blockchain Knowledge - Popular Edition", "Blockchain Knowledge - Technical Popular Edition", "Turing Blockchain", "Blockchain Economic Model", "Web3.0: Building the Digital Future of the Metaverse"; and The 3 books on Ethereum are partially written and unpublished. These contents refer to a lot of native blockchain protocols, white papers, and technical principles. The output of these contents is also the result of everyone. I just collected and organized them. Slowly, I understood the correlation between these underlying principles and many technologies and possible future application scenarios.
(7) Discussion and thinking with team members when designing related products in our project.
I am very grateful to Mr. Dashan of SatoshiLab, Elaine Yang, Hong Shuning, and related technical experts. They read this article and gave a lot of feedback and revision opinions. They strictly controlled the accuracy of the concepts quoted in the article until we could find it. Only the original references will be confirmed as qualified. Appreciate this rigorous habit!
Many thanks to all contributors and participants who have improved my body of knowledge.
MEV Boost, Blob, The role of Blob, Reorgs and MEV-Boost Golden Finance, Analysis of the development and price stability of the Blob market
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceThe Ethereum network has reached one million validators, staking 32 million Ether. Community concerns arise over potential security issues and decentralization.
 Alex
AlexThis article provides an in-depth analysis of how AI is revolutionizing financial transactions and investments, demonstrates the application cases of the 3EX platform, and discusses the broad potential and impact of AI in the financial field in the future.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceGrayscale Research’s analysis shows that traditional balanced portfolios can achieve higher risk-adjusted returns with a modest allocation to cryptocurrencies (approximately 5% of total financial assets).
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceXRP Ledger validators approve Clawback for reversible transactions and back an upcoming AMM trading platform upgrade.
 Edmund
EdmundStablecoins have emerged as a prominent category within the cryptocurrency ecosystem, but why are they important?
 Bitcoinworld
BitcoinworldLatest data from Glassnode shows that the number of Ethereum validators observed a significant increase this month, adding 11.4k to the total.
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistBlockchains use consensus algorithms to choose who gets to verify transactions on the network — what are the differences between the two?
 Cointelegraph
CointelegraphThe Fed vice chair told the House Financial Services Committee that a CBDC offers stability, interoperability in increasingly complex economic system.
 Cointelegraph
CointelegraphCrypto Twitter discusses whether mining Bitcoin with clean energy offers a good solution to excess or unused energy.
 Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph