After the latest FOMC meeting ended on the 1st, the Federal Reserve (Fed) maintained the federal benchmark interest rate at 5.25%~5.5% for the eighth time as expected by the market. Fed Chairman Powell also said at the press conference that the long-awaited rate cut is imminent.
The UK cuts interest rates for the first time in four years
In addition, the Bank of England (BOE) also released its latest interest rate decision later on the 1st, announcing that it would cut the benchmark interest rate by one point from 5.25% to 5%, the first rate cut since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020.
Bitcoin once fell below $63,000
We know that after the Bitcoin and Ethereum spot ETFs were approved for listing by the US SEC, and Bitcoin completed its fourth halving in history in April, the rate cut is considered to be another major positive factor stimulating the rise of the cryptocurrency market.
However, after the Fed eased its interest rate cut and the Bank of England officially started to cut interest rates, Bitcoin not only lacked the momentum to rise, but continued to fall after 21:00 last night, reaching a low of $62,280. It even fell to the key position of 60,500 this morning, almost falling below the 60,000 mark. Currently, it has rebounded slightly to around 61,500, but the sentiment is still not optimistic.
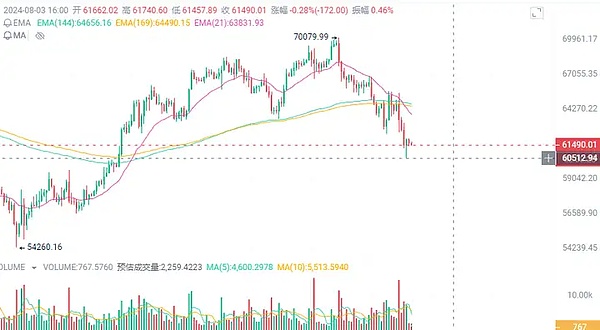
After rising the day before yesterday, US stocks also fell sharply last night. The semiconductor sector was particularly tragic, with Nvidia falling 7% and Arm plummeting 15%.
The US is about to cut interest rates, and the UK has already cut interest rates, but why is Bitcoin falling?
It will definitely fall after the interest rate cut?
Many investors may feel frustrated. Why is the market not responding to the increasingly clear expectations of interest rate cuts, but instead falling? Can interest rate cuts really stimulate the venture capital market every time?
Let's take a look at the changes in the stock market after the Fed's first interest rate cut.
Decline:
During the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, the stock market fell sharply in a short period of time after the interest rate cut, but it rebounded quickly
Before the 2008 financial tsunami, the interest rate was cut, and the stock market fell sharply afterwards
During the Internet bubble in 2000, the SP500 index also fell in sync with the interest rate.
Rise:
In 1995, the stock market rose after the interest rate cut
In 1989, the stock market rose slightly after the interest rate cut
In the stage of stopping interest rate hikes, the rise was mostly
It is worth noting that we can find that in each cycle, the S&P500 has shown an upward trend in the stage of stopping interest rate hikes. In 1995 and 2006, both rose by nearly 20%. The high interest rate maintained after August 2022 also allowed the US stock market to continue to set new highs; when the interest rate cut really began, a higher proportion fell.
One possible reason is the expectation psychology: in the stage of stopping interest rate hikes, the expectation of interest rate cuts is played out in advance, just like the market has often claimed that interest rate cuts are coming in the past year. Every time you see Powell constantly stating that the economic data should be taken as the standard, once the interest rate is really cut, the market has reacted in advance, and it is easy to run out of benefits.
On the other hand, the Fed has initiated interest rate cuts many times because of more serious economic problems, forcing the Fed to release money, which is not good news for the investment market.
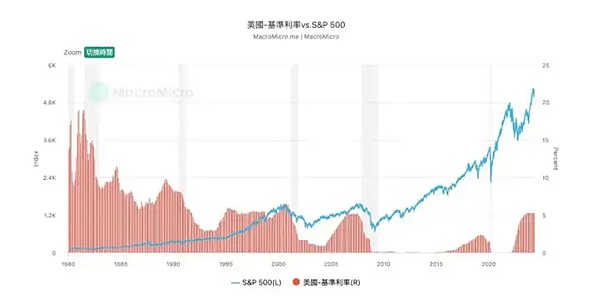
Back to this round of interest rate cuts, although the background of this interest rate cut is basically to return to normal, it cannot be ruled out that investors may sell assets due to potential "economic recession" expectations. Therefore, investors cannot simply follow the crazy market after the epidemic and think that interest rate cuts will definitely stimulate the stock market (or risk market) to rise.
The market fluctuates greatly in the short term, but only in the long term is it bullish
Therefore, although historical data shows that interest rate cuts are usually bullish for risk markets in the long run, it may take months to years for the fermentation period to break out of the rising market; short-term fluctuations are difficult to predict, and the market may reverse and fall instead. Bitcoin's decline last night may also be the first to fluctuate as a leading indicator, and how the market will perform in the future remains to be seen.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Weiliang
Weiliang JinseFinance
JinseFinance Edmund
Edmund JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Kikyo
Kikyo 链向资讯
链向资讯