Author: Shailey Singh, CoinTelegraph; Compiler: Deng Tong, Golden Finance
1. Understanding Compressed NFT
Compressed NFT is a non-fungible token (NFT) designed to reduce the cost of storing and using NFTs for transactions on the Solana blockchain.
As the adoption of NFTs continues to increase, developers are faced with the difficulty of maximizing storage and reducing the cost of minting these digital assets. The Solana blockchain introduces compressed NFTs (cNFTs) to overcome these challenges.
CNFT is a newer non-fungible token that uses state compression technology to store data more efficiently on Solana. Unlike traditional NFTs that store all token metadata directly on the chain or through external links such as IPFS, cNFTs use Merkle trees to optimize data storage.
In short, while regular NFTs store separate ownership and metadata records for each token on the chain, cNFTs group these records in a highly compressed format. This greatly reduces storage costs and increases transaction speeds.
While the technology is still in its infancy, it accounts for the majority of NFTs minted on Solana.
Second, the main features of compressed NFTs
With cNFTs, artists and developers can mint thousands or even millions of tokens at a fraction of the cost of traditional NFTs, thereby promoting innovation.
Let's take a look at some of the main features and advantages of cNFTs:
Cost-effectiveness:The cost of minting thousands of compressed NFTs is only a fraction of that of regular NFTs. For example, according to Solana's report, it takes about 24,000 to create and mint 1 million traditional NFTs using traditional metadata paths. cNFTs can be organized so that the same setup and minting costs are 10 SOL or less. This means that anyone who uses NFTs on a large scale can use cNFTs instead of standard NFTs, reducing costs by more than 1,000 times. Helius’ research shows a cost comparison of compressed and uncompressed NFTs as shown below:
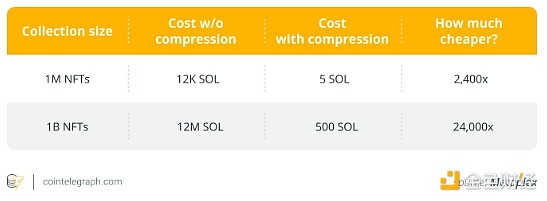
Scalability:Designed for high-volume use cases such as gaming, social media, and metaverse assets, which may require thousands or millions of tokens.
On-chain and off-chain flexibility:While ownership is tracked on-chain, much of the metadata can be stored off-chain, further reducing costs without sacrificing utility.
Compressed NFTs offer several key advantages that stand out in the blockchain ecosystem. They are affordable and significantly reduce the cost of minting and storage, enabling creators and businesses to use blockchain technology without financial barriers.
In addition, cNFTs contribute to greener blockchain practices by reducing storage requirements and, therefore, energy usage. These attributes make cNFTs a potential game changer for scalable, environmentally friendly, and innovative applications.
3. Compressed NFTs vs. Regular NFTs
While both cNFTs and traditional NFTs are designed to tokenize digital assets, their designs and use cases are very different.
Traditional NFTs are known for their uniqueness and exclusivity, but their minting and storage costs can be prohibitively high for large-scale applications. Compressed NFTs solve this problem by leveraging state compression, significantly reducing costs and enabling affordable mass production of tokens.
Unlike traditional NFTs, which typically store all data on-chain, cNFTs offload metadata to off-chain systems, minimizing blockchain storage requirements while maintaining practicality.
Some key differences include:
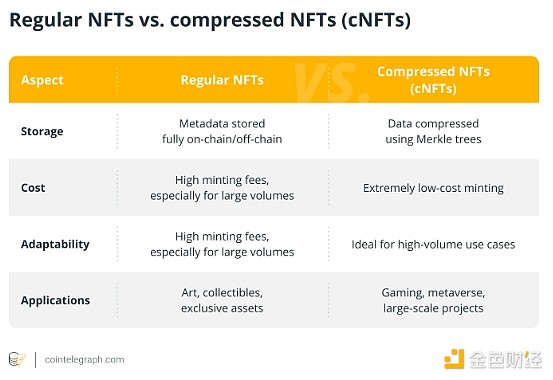
Regular NFTs are best suited for high-value, one-of-a-kind digital artworks or collectibles. Compressed NFTs, on the other hand, excel in scenarios that require high scalability, such as distributing gaming assets or digital collectibles to millions of users.
How to mint cNFTs: a step-by-step guide
CNFTs use state compression and Merkle trees to store data in a compact format.
Minting cNFTs may seem difficult at first glance, but with the right tools and knowledge, minting and distribution are simple. While each platform has its own instructions, here is a general guide to getting started with cNFTs:
Step 1:Set up a wallet: Use a Solana-compatible wallet like Phantom or Solflare to manage your funds and interact with blockchain tools.
Step 2:Fund your wallet: Add SOL, Solana’s native cryptocurrency, to cover the cost of minting. cNFTs are highly cost-effective, so even a small amount should be enough.
Step 3:Choose a minting platform: Platforms like Crossmint, Metaplex, and Candy Machine (on Solana) support cNFTs. Choose one based on the scale and functionality of your project.
Step 4:Prepare metadata: Define the details of your NFT collection, including artwork, description, properties, and other metadata. If needed, use an off-chain storage solution like IPFS.
Step 5:Mint your cNFT and set up a Merkle tree: CNFT uses a Merkle tree to organize data. Most minting platforms automate this process. Follow the platform’s interface to mint your compressed NFT. Confirm the transaction through your wallet and voila! Your cNFT is live!
Where are compressed NFTs stored?
Unlike regular NFTs, in cNFTs, the Merkle root is stored on-chain, while the Merkle leaves are stored off-chain.
CNFTs utilize a hybrid storage model that balances on-chain and off-chain storage, ensuring cost efficiency and scalability. The ownership of cNFTs is always tracked on-chain, ensuring the authenticity and provenance of the asset.
Nevertheless, most of the metadata of an asset, including images or detailed information, is typically stored off-chain. This decentralized off-chain storage often uses protocols like IPFS to ensure that data is distributed and accessible to anyone.
This combination of on-chain ownership and off-chain metadata helps to significantly reduce costs, as storing large amounts of data directly on the blockchain can be expensive and inefficient.
For Solana’s cNFTs, metadata is compressed and stored in a way that significantly reduces the storage requirements of the blockchain while maintaining the integrity of the asset information.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance






